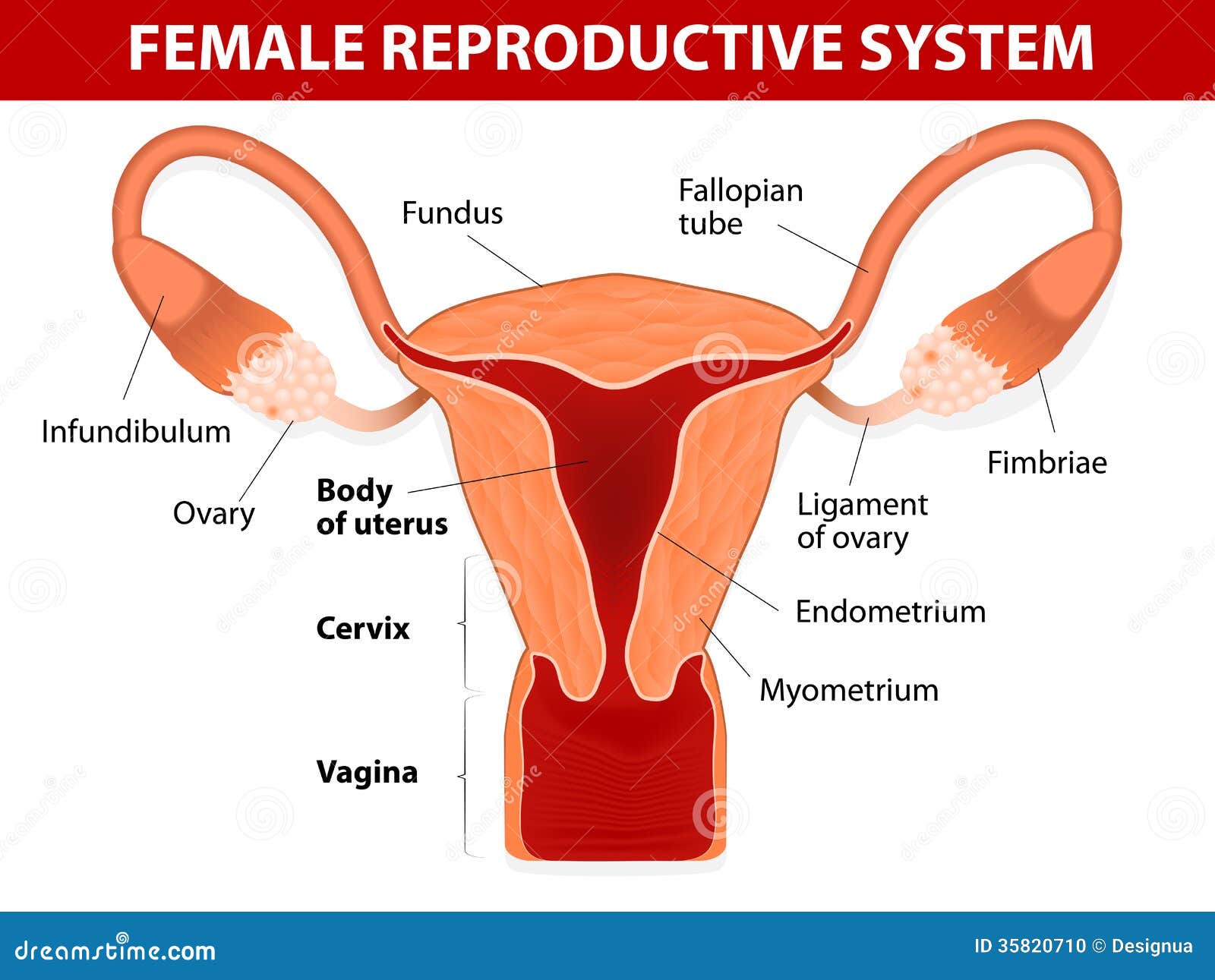
Labelled Diagram Of Fallopian Tube

The fallopian tube is composed of four parts.
Labelled diagram of fallopian tube. Every month your ovaries shoot out an egg and send it floating happily down the uterus where it will hang around in hopes of meeting up with some sperm to make a baby. 2 draw a neat and labelled diagram showing histology of uterus and fallopian tube. The channel of the tube is lined with a layer of mucous membrane that has many folds and papillae small cone shaped projections of tissue. Describe identify the microanatomical features of uterus and fallopian tube.
Fallopian tubes and ovaries. The innermost layer has spirally arranged fibres the middle layer has circular fibres and. Each fallopian tube is 10 13 cm 4 5 inches long and 0 5 1 2 cm 0 2 0 6 inch in diameter. The fallopian tube is connected to the body wall by the broad ligament which also contains the blood supply to the serosa.
Unless a biological abnormality surgery or ectopic pregnancy caused the loss of one tube women should have two. Female anatomy includes the external genitals or the vulva and the internal reproductive organs. Salpingectomy is the surgical removal of one unilateral or both bilateral fallopian tubes. They are present bilaterally at the superior part of the uterine cavity.
They provide a site for fertilisation and are involved in the transport of the ovum from the ovaries to the body of the uterus. Over the mucous membrane are three layers of muscle tissue. Fallopian tubes allow eggs to travel from the ovaries to the uterus. They are located in the lower abdominal or pelvic cavity of the female body.
Where are fallopian tubes located. Take a look at this low power image of the fallopian tube. Fallopian tube labelled diagram. The uterine tube fallopian tube carries an egg from the ovary to the uterus.
Can you identify the serosa adventitia layer muscularis mucosa layer the mucosa which is very highly folded longitudinally and the lumen the folded mucosa are where the ova are fertilised. A part of uterine tubes called the ampulla is where the female eggs get fertilised by the male sperm. June 30 2020 the fallopian tubes are important structures in the female reproductive tract which connect the peritoneal cavity with the uterine cavity. This article looks at female body parts and their functions and it provides an interactive diagram.
These are described from near the ovaries to inwards near the uterus the infundibulum with its associated fimbriae near the ovary the ampulla that represents the major portion of the lateral tube the isthmus which is the narrower part of the tube that links to the uterus and the interstitial or intramural part the narrowest part.